연소, 가열담배 흡연자와 금연자의 건강행동
Health Behaviors in Combustible Cigarette, Heated Tobacco Users and Quitters
Article information
Trans Abstract
It is important to identify health behaviors in smoking, because smoking habit can be changed by health behavior education on the fact that unhealthy behaviors can cause chronic diseases and cancer. We try to compare the health behaviors of combustible cigarette (CC), heated tobacco (HT) users, and quitters. Smoking behaviors were divided into three groups (CC, HT users, and quitters). The HT user group (n = 100) was selected among those who underwent a health examination in 2021-2022. CC smokers cohort group (n = 100) and quitters cohort (n = 100) were randomly selected from the same groups (age ± 2) who underwent a health examination in the same period. Sleep-related problems (snoring and sleep apnea), alcohol consumption, and exercise were compared in the CC group, HT group, and quitters group, respectively. Snoring was more common in the quitters group (27%) than in the CC users group (19%) and HT users group (18%). It can be related to weight gain during quitting tobacco use. Nondrinkers were more common in the CC users group (21%) than the HT users group (8%) and quitters group (10%). CC users seem to be more concerned about the health effects of drinking compared to HT users and quitters. Anaerobic exercise was different among groups, and aerobic exercise was not. HT users group did more aerobic exercise than CC users and quitters group. Differences in healthy behaviors among CC and HC users and quitters can be useful information for health education to smokers. Understanding smokers’ health behavior is important to smoking cessation counseling in clinical practice.
Introduction
Tobacco smoking is proven as the leading preventable cause of death, and kills more than 6 million people in a year [1]. Most adult combustible cigarette (CC) smokers want to quit, but the addictive nature of nicotine makes it difficult [2]. And many smokers try to find less harmful heated, non-burn tobacco products. While heated tobacco is not harm-free [3], it yields significantly lower concentrations of carcinogens and other toxins than combustible cigarettes [4], and is marketed as a less harmful alternative to cigarettes. This reduced-harm designation may account for much of their popularity among adult smokers, who commonly report using e-cigarettes as “healthier” substitutes for a cigarette. Heated tobacco (HT) users were 13.6% of male adults in Korea [5].
Understanding smokers’ health behaviors will be important for cessation counseling. The health behavior model shows that people are motivated by various healthy behavior education, and smoking and inactivity can be changed by health education [6]. Health behaviors can be improved by educating them on the fact that unhealthy behaviors can cause chronic diseases and cancer in primary medical care, and that it is important to identify health behaviors for holistic treatment [7].
In this study, we try to compare the health behaviors of CC, HT users and quitters.
Method
Smoking behaviors were divided into three groups (CC, HT users, and quitters) among male smokers and 100 subjects were recruited in each group. The HT user group (n = 100) was selected among those who underwent a health examination in 2021~2022. CC smokers group (n = 100) were randomly selected from the same age (± 2) who underwent a health examination in the same period. Quitters cohort (n = 100) were randomly selected from the same age (± 2) who had quit smoking within the last 10 years. We excluded people with serious illnesses that may affect study results and groups with missing values in the self-reported health behavior questionnaire.
Smoking history, disease history, snoring and sleep apnea, alcohol consumption, and exercise were compared in the CC, HT, and quitters group, respectively. For drinking, the frequency was recorded by number of weekly, monthly, and yearly drinks. And the types of alcohol mainly consumed were identified to as soju, beer, rice wine, wine, etc. Drinking more than once a week and drinking more than 3 drinks at a time was classified as unhealthy (problem) drinking. Exercise was divided into high-intensity, medium-intensity, and strength training, and the average number of exercise days per week and the duration of exercise per session were examined. It was divided into non-exercise group, exercise group 1-2 times a week, and exercise group 3 or more times a week.
This study was conducted after receiving approval from the Research Ethics Review Committee of Keimyung University Dongsan Hospital (2022-06-047). Statistical analysis was used by IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 23.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA), and composite sample X2 test, a composite sample general linear model was analyzed using a paired t-test. P values are calculated by analysis of variance or Fisher’s exact test.
Result
Study characteristics among combustible cigarette, heated tobacco users, and quitters
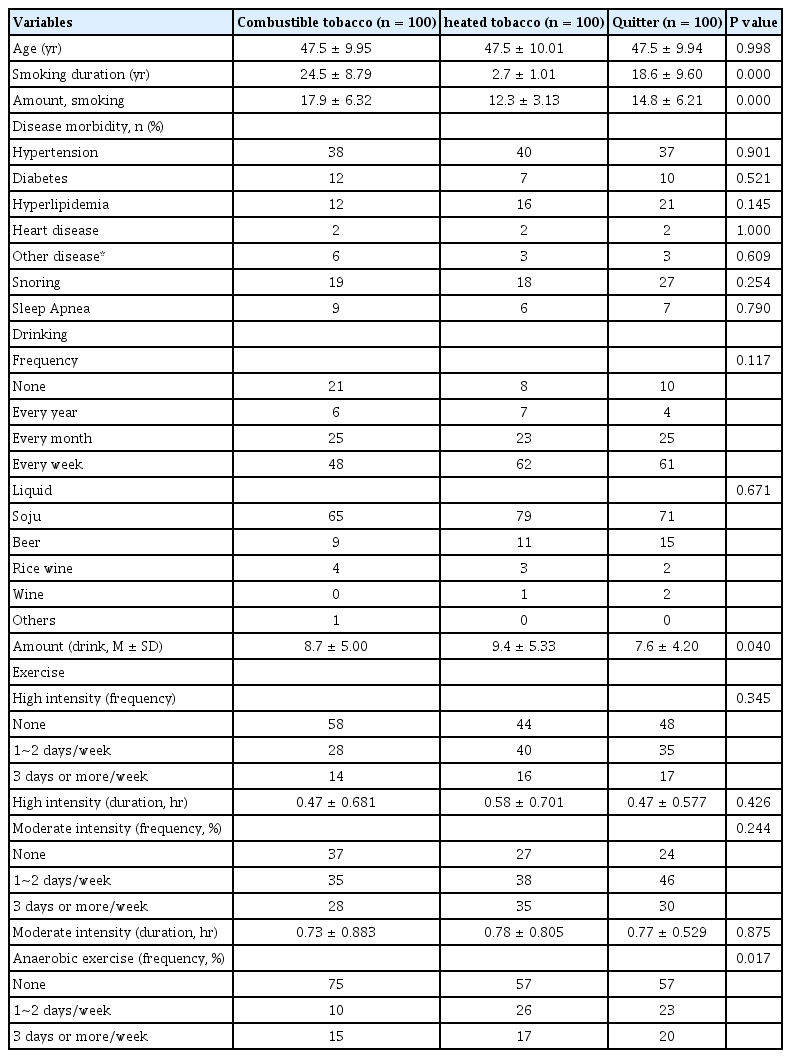
A total of 300 adult males (100 combustible, 100 heated tobacco users, and 100 quitters) were included in smoking behavior cohorts in January 2021-October 2022. The mean age was 47.5 and smoking amount and duration were 17.9/day and 25 years in the CC users group, 12.3/day and 12.3 years in the HT users group. The Mean duration after quitting smoking was 4.8 years in the quitters group.
Comorbid chronic diseases were hypertension (19%), diabetes (10%), and hyperlipidemia (17%). Heart disease (2%), gout, and vertebral disc disease. Snoring is present in 21.3% and more common in the quitters group (27%) compared to the CC and HT smoking group (18.5%). Sleep apnea was present in 7.3% (22/300). Table 1 shows the drinking and exercise habits of the three groups.
Health behavior between combustible cigarette and heated tobacco users
Comparing CC and HT users groups, nondrinkers were more common in the CC users group (21% vs. 8%) and regular drinkers were more common in the HT users group (48% vs. 62%). The exercise (high and moderate intensity) amount and frequency were not different between CC and HT users groups. But the HT users group did more anaerobic exercise than the CC users group (43% vs. 25%) (Table 2).
Healthy behavior between combustible cigarette users and Quitters
Snoring was more common in the quitters group than in the CC users group (27% vs. 19%). Sleep apnea was not different between the CC users group and the quitters group. Nondrinkers were more common in the CC users group (21% vs. 10%) and regular drinkers were more common in the quitters group (48% vs. 61%). Exercise (high and moderate intensity) amount and frequency were not different between the CC and heated tobacco users groups. But the CC users group did less anaerobic exercise than the quitters group (25% vs. 43%) (Table 2).
Healthy behavior between heated tobacco users and quitters
Snoring was more common in the quitters group than the HT users group (27% vs. 18%). Sleep apnea was not different between the HT users group and quitters group. Drinking frequency and amount were not different between the HT users group and the quitters group. And exercise (high, moderate intensity, and anaerobic) amount and frequency were not different between HT and quitters groups (Table 2).
Discussion
This study evaluated the healthy behaviors among the CC, HT, and quitters group. Sleep-related health behavior, alcohol use, and physical activity were compared according to smoking behaviors to understand and educate health behaviors. Health behavior known to be improved by educating unhealthy behaviors can cause chronic diseases and cancers [8].
In sleep health behavior, snoring was more common in the quitters group (27%) than in the CC users group (19%) and HT users group (18%). It can be related with weight gain during quitting tobacco use, and cessation-related weight gain can be prevented by exercise [9].
In alcohol-related health behavior, nondrinkers were more common in the CC users group (21%) than in the HT users group (8%) and quitters group (10%). CC users seem to be more concerned about the health effects of drinking compared to HT users and quitters group.
In exercise-related health behavior, anaerobic exercise was different among groups, and aerobic exercise was not. The HT users group did more aerobic exercise than the CC users and quitters group.
It is known that the toxic substances of HT are less than that of general CC, but the effect on disease or cancer prevention has not been verified [10]. HT users are associated with lower engagement in risky behaviors, but not better health status or higher engagement in protective health behaviors, compared to CC smoking. And in HT users, alcohol use and unhealthy diet correlated with heavier use and may be important targets for preventing escalation to more harmful tobacco use [11]. As HT users perceived their health as better than CC users, health educators should understand the scientific uncertainty surrounding the use of HT and consider how to educate the information [12].
Studies examined differences in healthy behaviors among CC, HC users, and quitters was very scarce. Most studies that report an association between smokers and risky health behaviors have focused on associations with the likelihood of CC. This study contributes new information to this literature and may yield important insights into potential variability among CC users with respect to health behaviors. This difference in health behaviors between each smoking behavior can be used in health education in CC and HC users.
Prospective observation needs to be done to clarify health behavior and health states among CC, HT users, and quitters.
Notes
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts-of-interest related to this article.